INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY LAW AND COMPETITION LAW
PUBLISHED ON 19.11.2021 BY MS. APARNA JAIN, MS. HARINDER NARVAN, MS. AASHRIKA AHUJA AND MR. KARANVEER SINGH
INTRODUCTION
The Competition Act, 2002 was enacted by the Parliament of India to govern the Indian Competition Law. The Competition Law regulates the competition between different entities so that there is no adverse effect on the market by influential entities creating monopoly. The Competition Act, 2002 replaced The Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 which was intended to curb the rise of concentration of wealth in a few hands and of monopolistic practices. Under the present legislation, the Competition Commission of India was enacted which was established to prevent the activities that have an adverse effect on competition in India. Thus, the Competition Commission of India regulates competition in India. The Competition Commission of India is duty bound to protect the interests of free and fair competition in the market, thereby, protect the interests of the consumers. There are several duties of Competition Commission of India which are to prohibit the agreements or practices that have or are likely to have an appreciable adverse effect on competition in the market in India; to prohibit the abuse of dominance in the market and to prohibit acquisitions, mergers, amalgamations etc. between enterprises which have or likely to have an appreciable adverse effect on competition in the market.
As far as intellectual property rights regime is concerned, it exhibits the characteristics of inherently being pro competitive as consumers can make choices between competing entrepreneurs and their goods and services. But the goal of both intellectual property rights regime and competition policy is economic efficiency and welfare. Intellectual Property regime’s support for technological innovation as well as competition law’s aims to support strategies that support product growth lead enabling both competition policy and IPR regime come at a common platform instead of being at crossroads which is the most popular myth among both the industries. At Knowledgentia, which is top law firm for global IPR protection, our experts offer advisory where our clients can harmonies with competition policy of the government along with protecting and strengthening their IPR.
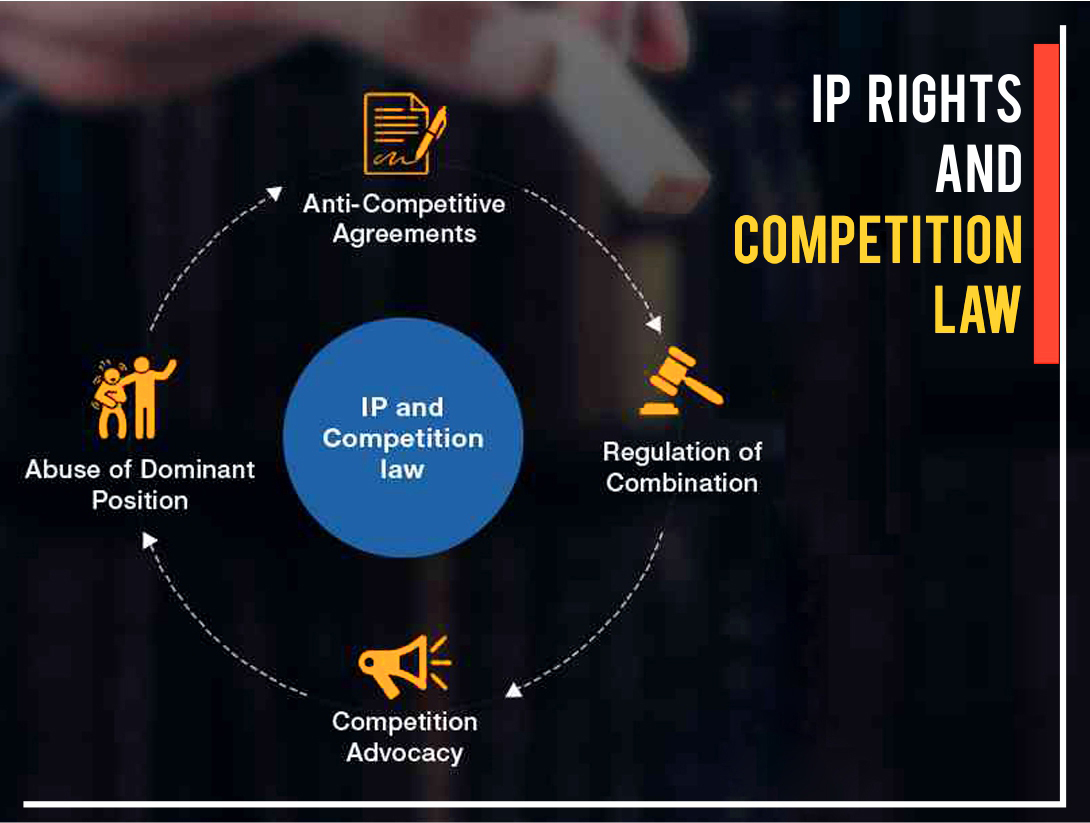
INTERPLAY BETWEEN THE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY LAW AND THE COMPETITION LAW IN INDIA
The Competition Law deals with an efficient mechanism to counter anti-competitive agreements, whereby, regulating mergers and acquisitions, restricting the use of dominant position etc. of enterprises in the market, whereas, the Intellectual Property Law tries to strike a balance between the rights of the owner and as well as the social interest of the public at large. Intellectual Property Rights helps the owner of the intangible property to get an exclusive right and monopoly over his creation, also, promoting the competition within the market.
Intellectual Property Law gives exclusive rights and monopoly to which Competition Law disagree, but the Intellectual Property only grants a durational limited monopoly, whereby, preventing the creation of unlimited dominant position in the market for perpetuity. It is important to boost the spirit of the creator on one hand and also to control the competitiveness in the market on the other hand. The Intellectual Property Law and the Competition Law are complementary in nature. Intellectual Property Rights provides a chance to the creator for a technological innovation and protection, which boosts the confidence in the market creating a healthy competition. This leads to a dynamic growth of the market, which is considered as one of the main aims of the Competition Policy.
Generally, the Intellectual Property Law and the Competition Law have conflicting objectives. The reason behind this conflict is that Intellectual Property creates limits in the market within which competitors may be unable to exercise certain rights over the invention, thereby, creating monopolies in favour of one enterprise. This limitation seems to be against the market access and level playing fields under the Competition Law, specifically restricting the competitors, thereby, enjoying the monopoly position in the market. The primary objective of the Competition Law is to stop the abusive practices in the market, stipulate and encourage competition in the market and make sure that the customer interest is protected, whereby, providing them goods or services at an affordable price with improved quality.
The correlation between the Intellectual Property Law and the Competition Law seems to be contradictory to each other but in actuality the Intellectual Property Law compliments with the Competition Law. The Intellectual Property Law gives benefits to the creator or inventor to enjoy exclusive rights for a particular period, thus, creating healthy competition in the market for present and future generations. The dominance and right to enjoy under the Intellectual Property Law will not lead to infringement of the Competition Law.
The Section 3 of The Competition Act, 2002 restrains any enterprise to enter into an agreement which will hurt the competition, thereby, protecting the spirit of the Competition Law. The Section 3 (5) of the Act lays down an exception, that the Competition Law does not affect the Intellectual Property Rights. But if we study the Section 3 (5) with the Section 4 then we find that it also restrains the Intellectual Property Rights holders to abuse their dominant position, thereby, the Competition Law coming into effect. Therefore, it can be concluded that both the Intellectual Property Law and the Competition Law are complimentary to each other rather than contradictory.
LANDMARK CASES RELATED TO THE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY LAW AND THE COMPETITION LAW
- Aamir Khan Production Private Limited v. The Union of India
18 August, 2010 by High Court of Judicature at Bombay
The Bombay High Court in this case held that the Competition Commission of India has jurisdiction to look into the matters of Competition Law and Intellectual Property Rights.
- Valle Peruman and others v. Godfrey Phillips India Limited
986 AIR 806, 1985 SCR Supp. (3) 123
Herein, the trademark owner misused the trademark by manipulating, and distorting. The court held that it amounts to unfair trade practices of the trademarks. The court while taking into consideration the Competition Policy of India stated that all kinds of Intellectual Property have the potential to infringe the Competition Law. The court also further observed that a trademark owner has the right to use his trademark in a reasonable manner subject to the conditions imposed at the time of granting a patent.
- Kingfisher v. Competition Commission of India
Laws (BOM)-2010-3-261
The court held that Section 3 (5) does not limit the right of the holder of Intellectual Property Rights to sue for infringement of the copyright, trademark, patent, etc. The Competition Law does put the bar on the application from the other law.
- FICCI Multiplex Association of India v. United Producers Distribution Forum
25 May, 2011 before The Competition Commission of India, New Delhi
In this case the main question was whether the competition in the market affects the right of the copyright holder. The court observed that the right granted to the copyright holder is not absolute right but it’s a statutory right under the Copyright Act, 1957.
- Entertainment Network (India) Limited v. Super Cassette Industries Ltd.
16 May, 2008 in the Supreme Court of India
In this case, the Supreme Court observed that the charge of royalty through an issue of license for the copyright owner is not an absolute right. If the patented product is priced very high then it will directly contradict the Competition Law and awarding a license only to one person upon application would go against the very spirit of the statute.
Concluding, it can be said that both the Intellectual Property Laws and the Competition Laws are complimentary to each other rather than contradictory and there is a harmonious interplay between the both. At Knowledgentia, which is the best corporate international law firm in India, we have experts who are well versed with all latest trends in the field of IPR and competition law thereby providing effective solutions for our clients and colleagues across the world. We are your one-stop solution for all kinds of legal, compliance and supplemental matters concerning all IPR matter. In case of any query regarding this matter you may email us at info@knowlegentia.com or visit our website -https://knowledgentia.com/.